
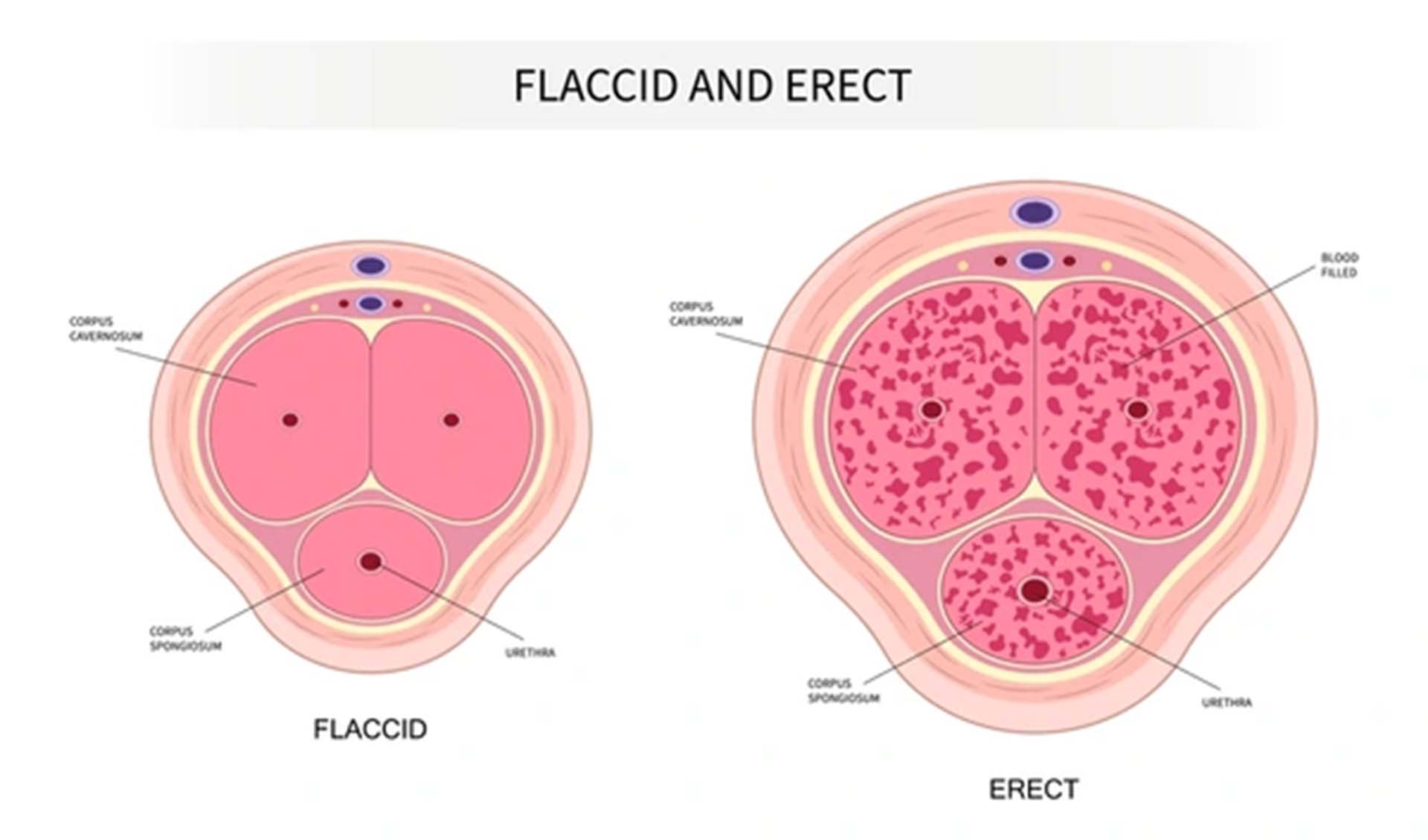
As mentioned, occasional episodes of not achieving erection, or not being able to maintain an erection can be normal. These can be due to temporary causes such as stress or fatigue. However, persistently having difficulties with achieving or maintaining an erection may require medical attention and treatment.
Research suggests that excessive alcohol intake and smoking shows a dose-dependent effect on erectile dysfunction. This means that the more you drink or smoke, the higher the risk of ED. Scientists suggested that both excessive alcohol intake and smoking leads to damage to the blood vessels, which may contribute to impaired blood flow into the vessels of the corpora cavernosa.
Studies reported that moderate and frequent exercise was linked to a lower risk of ED.
Obesity and other metabolic syndromes increase the risk of ED likely from comorbidities and complications such as hypogonadism and inflammation.
Diabetes can increase the risk of ED through complications such as peripheral neuropathy, atherosclerosis, and associated hypogonadism.
Cardiovascular diseases and ED have common causes due to underlying vascular disorders.
Researchers reported an increased association between patients with BPH/LUTS and ED.
Psychological disorders such as depression and anxiety, as well as the use of psychotropic drugs to treat these conditions are known to increase the risk of ED.
A Doppler ultrasound allows the doctor to observe blood circulation in the arteries and veins. This can identify possible blockages that may cause ED.